Sand Dams Literature Review
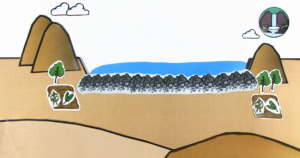
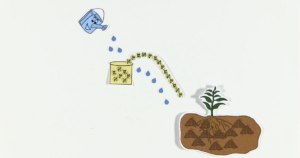
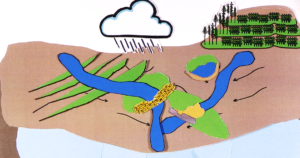
In arid and semi-arid regions of the world, sand storage dams can help store water during the rainy season for later use with easy accessibility for local residents. If constructed correctly, a sand storage dam can be a reliable water supply option. The following Literature Review gives you an overview on sand storage dams and most recent research on the topic.